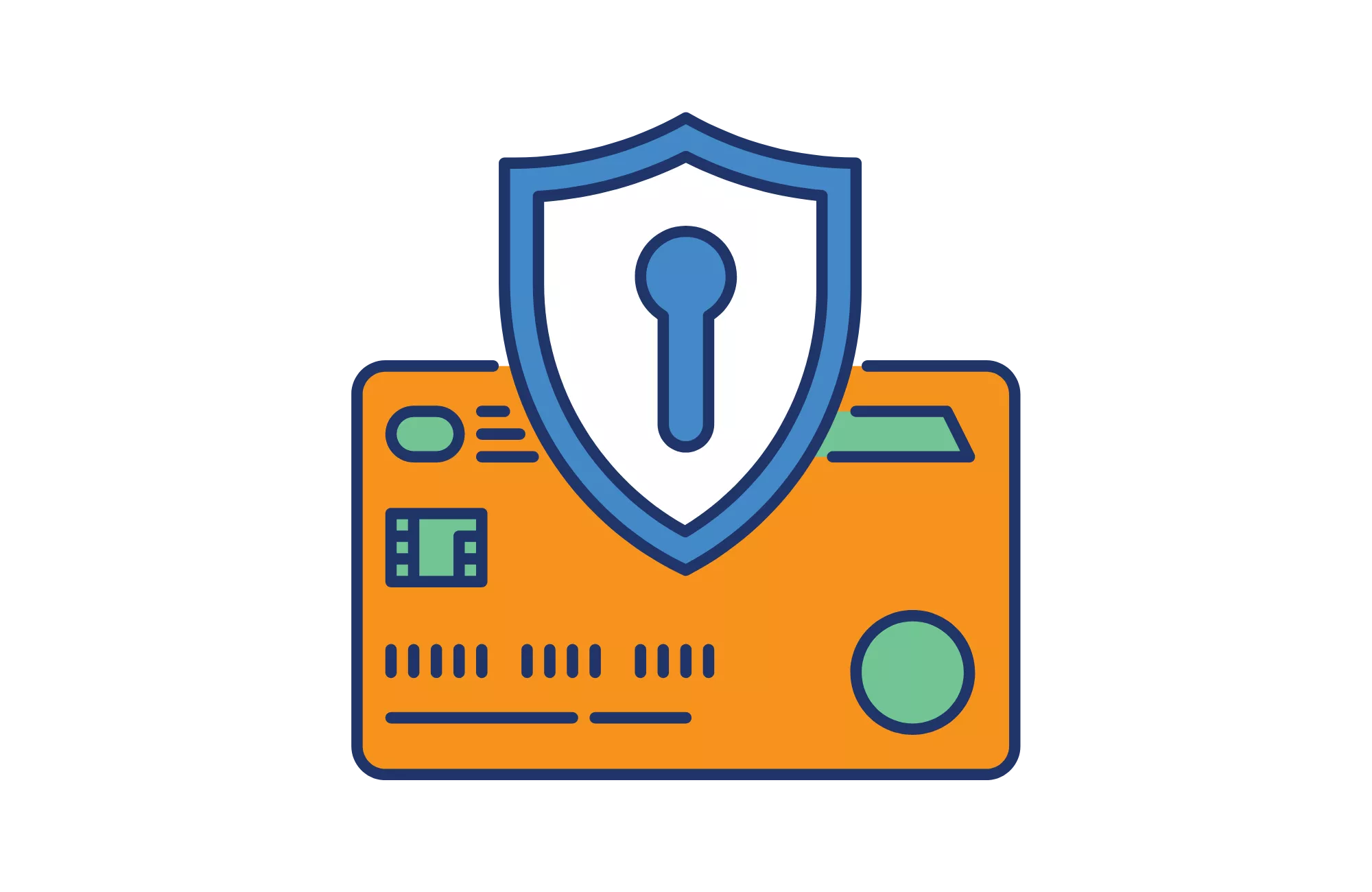
In today’s digital age, credit card fraud is a concern for consumers and business owners alike. Fortunately, credit card tokenization has emerged as a popular method to secure sensitive credit card data. This allows customers to shop online without fear their credit card information is at risk. Additionally, businesses that implement credit card tokenization benefit from increased customer trust, as they are demonstrating a commitment to protecting their customers’ sensitive financial data.
In this post, we explain exactly what credit card tokenization is, how it works, and why it’s a crucial security measure for businesses accepting credit cards.
What Is Credit Card Tokenization?

A software company, TrustCommerce, created credit card tokenization in 2001 to secure sensitive payment data for one of its clients. The tokenization of credit cards is an additional layer of protection that substitutes sensitive data with a sequence of numbers known as tokens.
This concept doesn’t only apply to credit card payments: Casinos, arcades, and carnivals all use unique tokens to replace real-life money and have no value except when used on their grounds. Similar tokenization concepts, such as the surrogate key, existed in the 70s, yet it wasn’t until the early 2000s that the tokenization we know today was created.
How Does Tokenization Work?
Tokenization works similarly to the way arcades manage their currency, where players exchange money for tokens that hold no value outside of the arcade. Likewise, payment tokenization transforms sensitive information into data that is meaningless to unauthorized parties.
When you tokenize credit cards, the process shields cardholders from fraud and other data breaches. It essentially replaces the primary account number (PAN) with a string of random numbers referred to as tokens. The tokens produced through tokenization can be used to process payments through various networks without disclosing your customers’ credit card information. While credit card EMV chips protect cardholders from fraud in brick-and-mortar stores, tokenization ensures safe online shopping.
Due to their lower level of security, merchants that store credit card data are more susceptible to data breaches than banks or payment networks. Tokenization is beneficial for merchants, as it helps them to enhance the security of their customers’ sensitive credit card information.
Payment Tokenization Examples
eCommerce
Tokenization is helpful for checkouts with stored credit card information as it prevents misuse in the event of a data breach. When storing card information, tokenization occurs automatically, ensuring that the issuing banks receive tokens instead of sensitive information. This makes it impossible to access card details in case of a data breach.
In-App Payments
Shopping apps can integrate with tokenized payment information directly stored on a mobile device. When a customer initiates an in-app payment, the token transmits to the payment processor, which retrieves the payment information. This avoids the need for consumers to input card numbers and ensures the payment method is secure.
Tokenization vs Encryption: What’s the Difference?
Credit card tokenization and credit card encryption are the most popular security measures against credit card fraud. Both tokenization and encryption protect sensitive credit card information through algorithmically-generated numbers. With encryption, an algorithm encodes the actual payment data. Meanwhile, with tokenization, the data swaps with a valueless token. Since there’s no useful information on a token, there’s also no risk of stolen information in the event of a data breach.
Encryption becomes increasingly difficult to crack as the algorithm becomes more sophisticated. However, if credit card information goes through a network, as it does for recurring payments, it allows malicious actors time to decode sensitive information.
The Benefits of Tokenized Credit Cards

Better Customer Experience
Customers are more likely to shop at your business if they know their data is safe. A business tokenizing credit cards shows its consumers that it values and protects their sensitive financial data.
Improved Payment Processing
Tokenizing payments helps detect credit card fraud and protect payment processing. And less fraud means there’s less of a chance for the occurrence of chargebacks.

Enhanced Security
Through tokenization, you offer the highest possible level of cardholder protection for many payment technologies. This is because when a cardholder makes a payment, the card details do not transmit to the payment gateway. Instead, a token is created that represents the card details.

PCI Compliance
Many businesses that store sensitive data on their systems find it challenging to comply with PCI DSS standards. Data breaches that happen to non-compliant businesses often lead to PCI non-compliance fees. Businesses risking the security of customer data are subject to this fee.
Final Thoughts on Tokenizing Payments
When it comes to credit card security, credit card tokens are a merchant’s best friend. It stops potential cyberattacks, data breaches, and hackers from accessing sensitive credit card information. Furthermore, tokenizing credit cards benefits a business by enhancing customer experience, supporting PCI compliance, and protecting one-click payments. If you’re considering credit card tokenization for your business, it’s important to find a reliable payment gateway that offers it. By partnering with a merchant services provider with payment gateway solutions, you can unlock boundless cardholder data protection benefits.
FAQs About Tokenization for Credit Cards
What does card not tokenized mean?
Expired credit cards produce this message. Sometimes, banks honor an expired card, but PCI compliance demands payment providers delete expired credit card information within six months of expiration. This results in the untokenization of the card.
How are tokens created?
By tokenizing a credit card, an algorithm or non-reversible cryptographic algorithm replaces a cardholder’s account number with a randomly generated number. The generated number is the token.
Is tokenization PCI-compliant?
Tokenization is a PCI-approved method of shielding sensitive credit card information. It’s authorized by the PCI Security Standards Council (SSC). For more information about tokenization being PCI-approved, check out the SSC guidelines on tokenization.
Is tokenized data reversible?
Unlike encryption, the data secured with tokenization is unreadable and irreversible because there’s no connection between the token and the data.
What does “card tokenization failure” mean?
Card tokenization failure appears when trying to tokenize an expired card. As tokens are used for card-on-file transactions, a typical tokenization failure can happen in the event that a consumer has completed an initial payment but their card expired before their payment information was updated.
What is token provisioning?
Token provisioning is when a payment provider (the token requester) requests the creation of a token for a primary account number (PAN). Payment providers use tokens for online and mobile payments.







