Churn rates are a crucial metric for any subscription services company. Understanding what churn is and how to measure it can help you make better decisions about your business. We’ve compiled the ultimate guide on churn rates, including definitions, causes of high churn rates, and how to lower them.
Small business owners, here’s what decreasing your churn rate will do for you:
- increase your customer life time value
- increase your monthly reoccuring revenue
- increase customer satisfaction
- increase revenue

What is Churn Rate?
The first step in understanding churn is knowing what it actually means. A churn rate, also referred to as customer churn rate or attrition rate, is the measure of the number of customers who discontinue their patronage or service with a company during a given time period. This is usually expressed as a percentage of the total customer base.
Why is it called ‘Customer Churn?’
When it comes to measuring churn, businesses typically measure their customers. However, that is a little misleading because there are actually two different types of customer churn: voluntary and involuntary.
Voluntary vs Involuntary Churn
Customer churn can be seen in two different ways, voluntary and involuntary. Voluntary customer churn is when customers decide to stop using your product or service on their own. Involuntary customer churn happens when customers are forced to leave against their will, such as if you discontinue a certain feature they enjoy using.
Attrition vs Churn
Although it may seem attrition and churn have different meanings, they are used interchangeably in the subscription business industry.
Arguably, attrition, or churn, is one of the most important KPIs to monitor as a business owner. It is critical to stay ahead of your attrition rate and ensure you are gaining more customers than you lose.
Gross Churn vs Net Churn
Customer churn can be viewed on two different levels, gross and net. Gross customer churn refers to the rate at which customers cancel subscriptions to your company or service provider, regardless of why they are leaving. Net customer churn takes into account the loss of customers/revenue due to cancellations or downgrades after taking the revenue from existing customers into account. For example, if you add 2 new customers a month, but you lose 2 customers a month, your gross customer churn is positive (lost 2 customers), but your net churn is neutral.
Customer Churn vs Revenue Churn
It’s important to note that revenue churn and customer churn are not the same. Customer churn is the measure of loss of customers whereas revenue churn is the measure of loss of revenue.
For example:
A customer downgrading their subscription would result in a higher revenue churn, but would not affect customer churn.
A customer upgrading their service would reduce revenue churn, but not affect customer churn as the business is now making more revenue.
What is Negative Churn?
Negative churn rates occur when you lose fewer customers than usual during a particular time period. For example, if your customer base is normally prone to attrition but you have an exceptionally good sales cycle that results in more new customers than usual, your rate of negative churn will be higher. This also occurs when you offer large discounts or other incentives, leaving your customers less likely to cancel their accounts.
Churn Rate vs Growth Rate
Churn rate and growth rate are two different concepts. Growth rate is the increase of your customer base over a given time period, such as year or month. Churn rate measures how many customers discontinue using your product or service during the same time period.
Churn Rate vs Retention Rate: Does Churn Affect Retention?
While they are different metrics, churn rate and retention rate typically go hand in hand. Retention refers to the number of customers who are still using your product or service by a certain date, while churn is the opposite. Churn does affect retention because it measures how many people leave during a particular period.
What is a Good Churn Rate?
This varies from industry to industry and company to company. There are many factors that go into what makes a good churn rate for your industry. For example, if your cost of acquisition is high, you need a lower churn rate to be profitable, but if your cost of acquisition is low, you can afford a higher churn rate and retain high-profit margins. Other factors include overhead costs, cost of goods sold, and lead generation costs. For instance, software-as-a-service (SaaS) companies can afford a higher churn rate, since they usually don’t have to deal with the costs of purchasing physical goods and handling logistics.
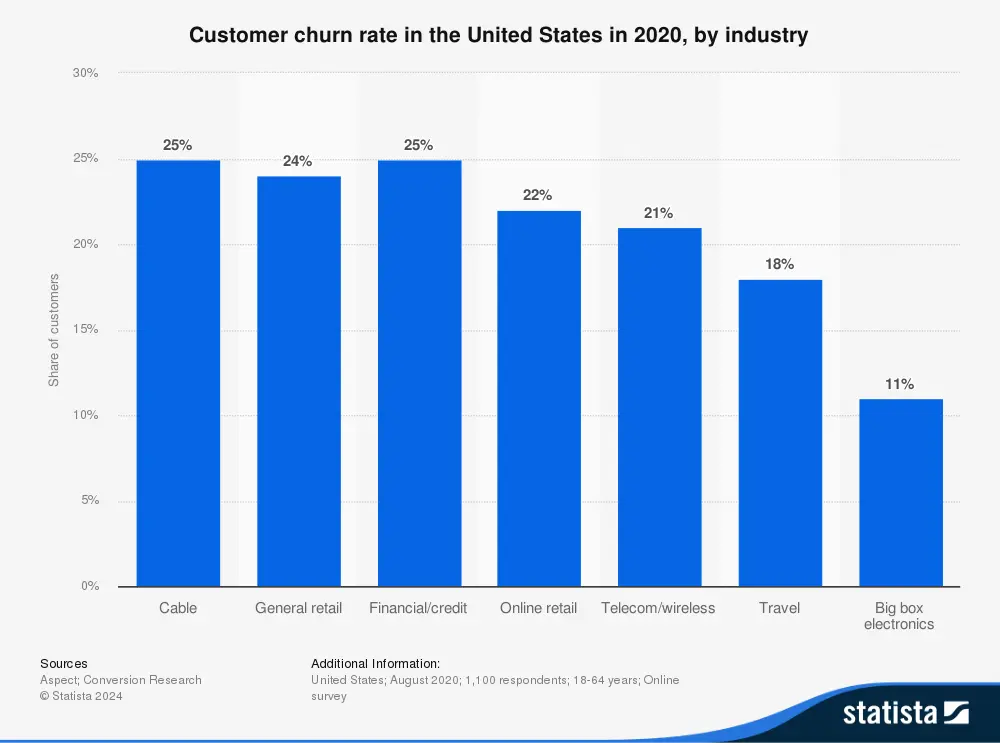
Average Churn Rates by Industry
While there is no universal benchmark for what the average customer churn rate should be, certain industries have higher rates than others. Due to varying factors, every industry’s churn rate is different.
What is Customer Churn Analysis?
Customer churn analysis is the process of examining your customer base and taking steps to improve retention. This often involves looking at specific data points such as how many customers you’re losing and why they’re leaving, then working on new strategies that offer better service or value to increase your number of retained customers over time.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Churn Rate
By performing customer churn analysis, you can identify the strengths and weaknesses of your company’s growth strategies. This information allows you to make changes that improve your business model for customers, leading to more improvements in retention over time.
Strengths
The primary strength of customer churn analysis is that it allows you to look at specific data points and see where you’re gaining customers and losing them. This information can be used to adjust your company’s growth model in order to increase both retention and revenue.
Weaknesses
The downside of churn analysis is that it cannot tell you what type of customer your business is losing. Churn rate does not show you the full picture, as it does not measure profitability and cannot tell you which areas you need to improve to increase profitability. You should not rely solely on churn rates to analyze your business’ success.
How to Calculate Churn Rate
There are two main ways to calculate customer churn rates. While the actual calculation may vary depending on your company, the end goal is to arrive at a number that represents how many customers you’ve lost or gained during a given time period (usually year or month).
Though there are a couple of ways to calculate churn, the simplest method is the following:
Churn Formula:
Lost Customers / Customers at the Begining of a period = churn rate
How to Reduce Customer Churn
Below are a couple of ways you can reduce your customer churn rates:
Focus on customer service
When customers leave negative feedback or reviews on surveys, think about where you can address their concerns and how you can use this information to improve your business. The value this kind of communication provides is immense; not only do these details help prioritize future repairs or re-campaigns but they also allow you to identify the reasons your customers leave and improve processes.
Maintain transparent prices and no hidden fees or costs
Be upfront with your customers and make sure they are provided the full list of fees and costs. You want to make sure your customer does not feel manipulated into paying for something they did not sign up for. This transparency will not only reduce churn but will also reduce the number of chargebacks you face.
Don’t charge cancellation fees
You should constantly look for ways to exceed your customers’ expectations. By always putting their needs first, you can be confident they will remain loyal. When facing retention issues, make a customer’s cancellation experience as smooth as possible. This will increase your chances of reactivating the customer in the future.
Offer ongoing discounts to customers as a retention strategy
The Correlation between Churn and CLTV
The correlation between customer lifetime value and churn rate is very strong. Reducing customer churn rate by 1% will increase average customer lifetime value by close to 1%. Therefore, it is important for companies to understand how changes in their churn rates affect their CLTVs so they can predict the impact of such changes. The lower churn you have, the higher lifetime value your business offers. You can reduce your business’s churn rate via the below suggestions:
Preventing Customer Churn: Keep Your Customers Interested
- Use social media as a marketing tool
- Utilize email marketing and email automation
- Offer free trials or money-back guarantees as a retention strategy
- Offer periodic discounts
- Listen to and address common feedback
- Prioritize your customer service response time
Final Thoughts

In the end, a churn rate is just the measure of how many customers you’ve lost or gained during a given time period. Metrics such as customer churn analysis allow continuity subscription merchants to identify their strengths and weaknesses in order to improve long-term retention. In today’s competitive business world, it pays off to have satisfied customers who come back for more purchases again and again. The key is being proactive about identifying and fulfilling your consumers’ wants so they don’t go looking for it elsewhere.
Sources: Profitwell, Statista, Kissmetrics, Chargebee




